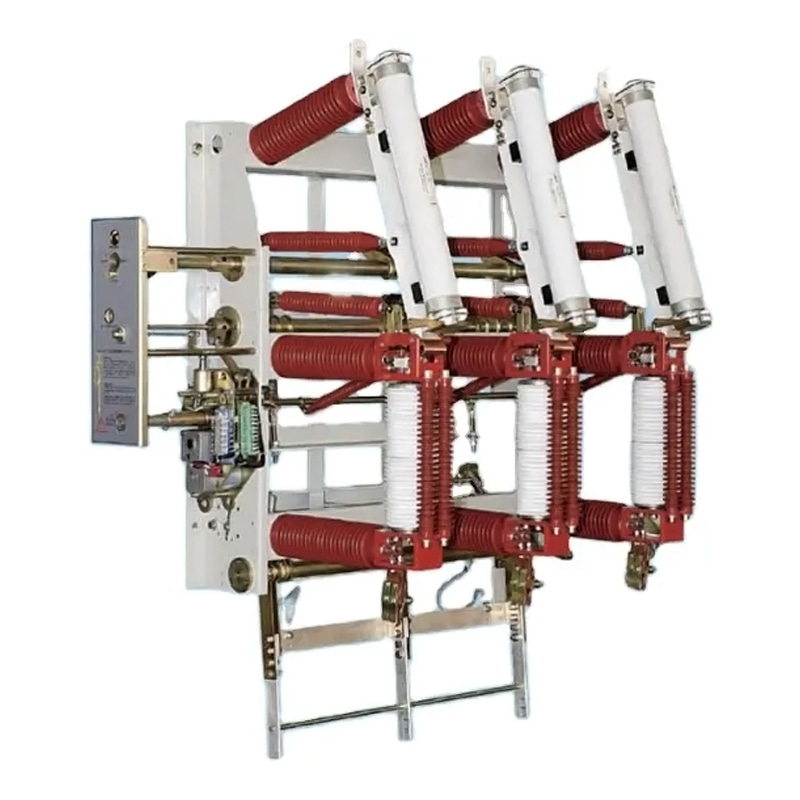
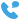
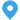
Every electrical system that handles energy distribution, whether industrial or commercial, depends on reliable mv & lv switchgear to protect circuits, isolate faults, and ensure continuity of power. In modern installations that span medium and low voltage networks, understanding how faults develop and what triggers them is crucial for engineers, technicians, and facility managers who deal with MV and LV power distribution systems daily. With the right insights into failure modes, you can safeguard uptime and reduce maintenance costs while optimizing system performance.
At Qinghang Electric Co., Ltd., we design our switchgear with a focus on reliability and serviceability. But even the best‑built equipment can experience issues if underlying causes aren’t addressed systematically. This article breaks down common fault types in medium voltage switchgear, explains underlying triggers, and offers practical insights for troubleshooting and prevention.
1. Mechanical Failures: Wear, Misalignment, and Moving Parts
One of the more common fault categories in medium voltage switchgear relates to mechanical components that fail to operate correctly. Breakers, interlocks, and other moving elements are designed to work reliably for many cycles. Nevertheless:
Components can wear out over time due to continuous operation.
Misalignment during installation or maintenance can prevent proper movement.
Excessive switching operations beyond design recommendations stress mechanisms.
When these issues occur, breakers may not open or close as expected, leaving parts of the distribution system unprotected and increasing the risk of equipment damage. Regular mechanical inspections and adherence to recommended operational cycles help mitigate these risks.
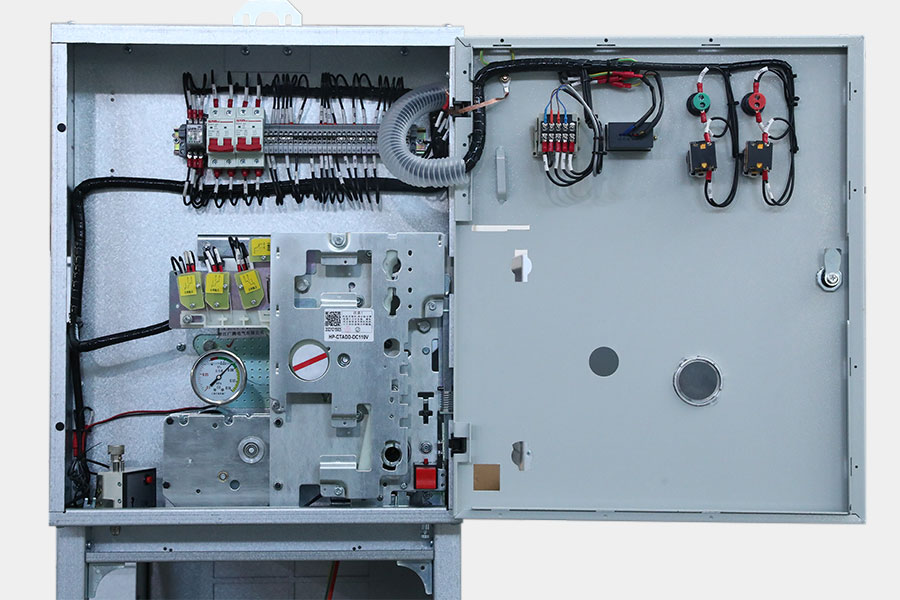
2. Electrical Faults: Short Circuits and Overcurrent Conditions
Faults within electrical circuits themselves are another significant trigger for switchgear issues. These typically occur when:
Insulation degrades due to age or environmental factors.
Contacts wear out or become contaminated.
Unexpected short circuits or overcurrents occur.
Electrical faults can cause protective devices to trip unexpectedly and may cause extensive downtime if not identified quickly. Integrating reliable protective relays and real‑time monitoring systems into your switchgear design allows for early detection and faster isolation of problematic circuits in MV and LV power distribution networks.
3. Thermal Problems Caused by Overheating
Heat is a silent enemy of electrical switchgear. Repeated exposure to high temperatures can degrade insulation, disturb electrical clearances, and reduce component life. Overheating may result from:
Load currents exceeding rated capacity.
Inadequate ventilation within the switchgear room.
Higher resistance caused by improper connections or aged components.
Installing temperature sensors and alarms within your switchgear setup enables proactive maintenance and helps you manage electrical load distribution to prevent heat‑induced faults.
4. Insulation Degradation: The Hidden Threat
Both MV and LV switchgear depend on robust insulation to maintain safe operation under voltage stress. However, insulation materials naturally deteriorate over time, and external factors such as humidity, dust, or chemical pollutants accelerate this process. When insulation strength weakens, systems are prone to partial discharges and increased risk of short circuits.
Routine resistance testing and preventive maintenance routines can help spot early signs of insulation decline before they become disruptive failures.
5. Control Circuit Malfunctions and Wiring Issues
Control circuitry, including relays, sensors, and wiring harnesses, manages the logic behind switching operations. If these elements fail due to loose connections, software errors, or power surges, switchgear can operate unpredictably — delaying fault clearing or even preventing protection operations altogether.
Periodically checking relays, tightening connections, and updating firmware where applicable are simple but effective ways to reduce control circuit‑related faults.
Faults in MV switchgear don’t have to be disruptive. By understanding the common causes — mechanical wear, electrical stress, thermal effects, insulation degradation, and control circuit issues — you can implement targeted preventive measures that save time and expense. For systems that integrate both mv & lv switchgear, a comprehensive maintenance plan paired with real‑time monitoring offers the ideal defense against unexpected outages. At Qinghang Electric Co., Ltd., we continuously refine our switchgear to address real‑world challenges and help our customers achieve steady, dependable power distribution across their networks.



 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى