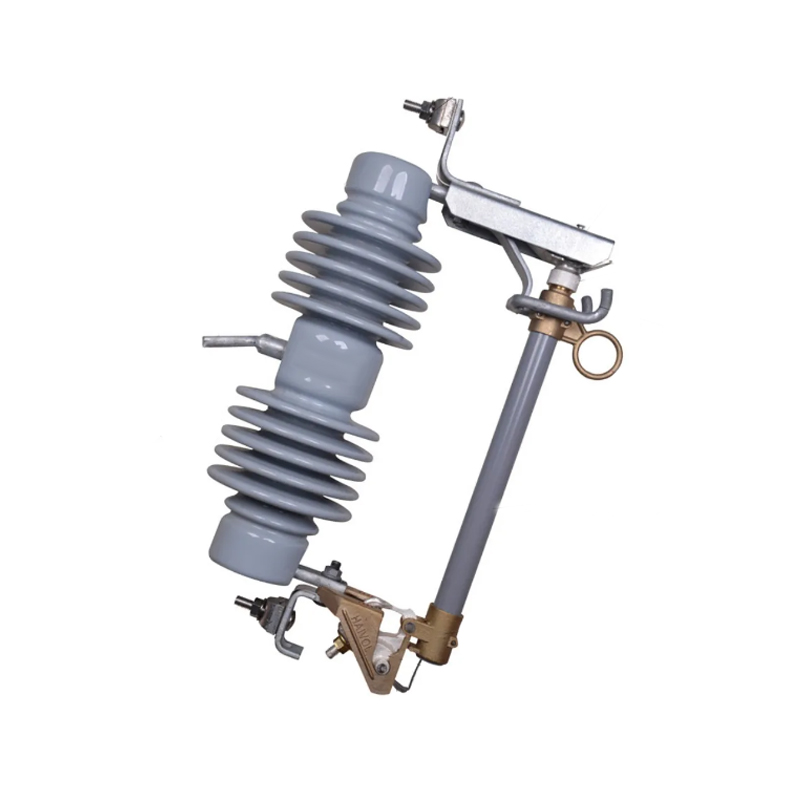
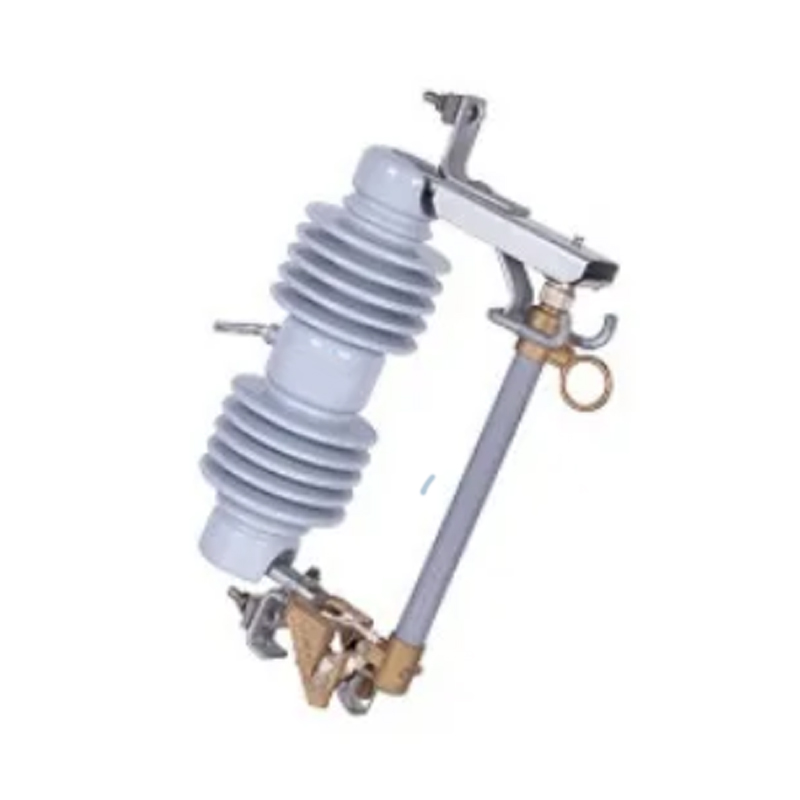
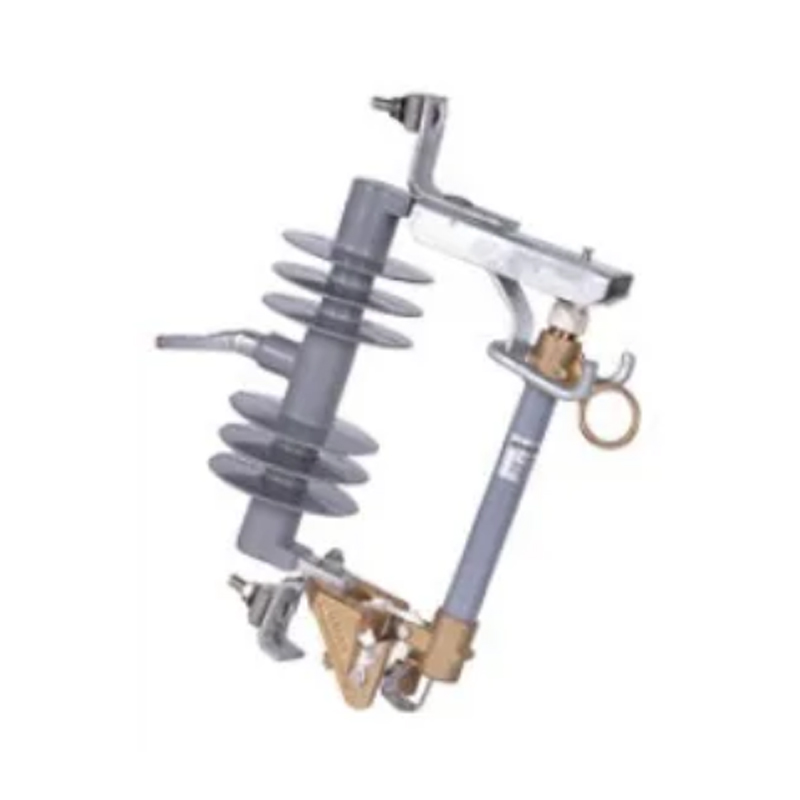
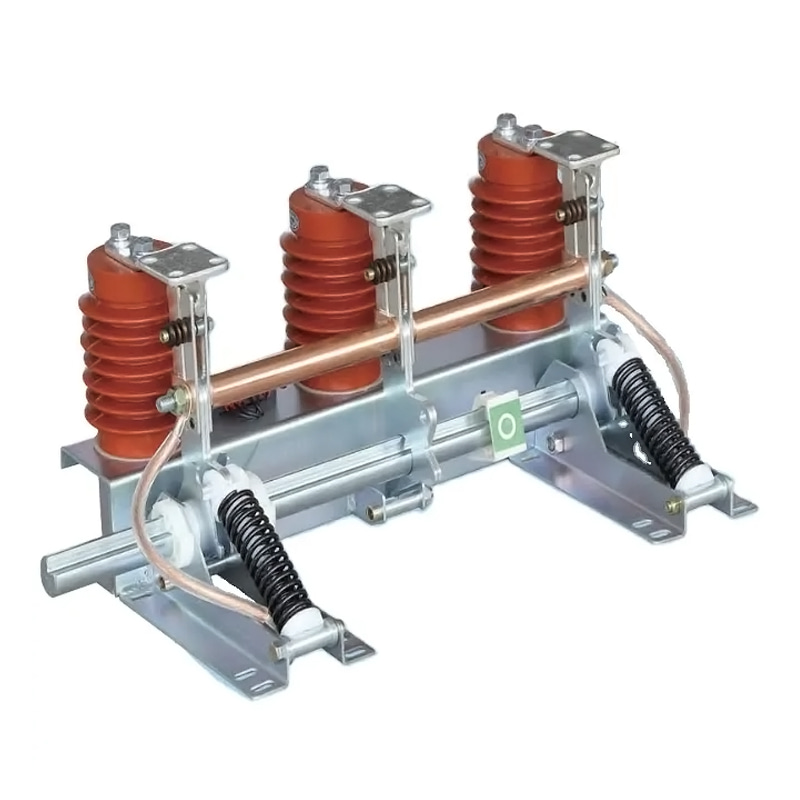
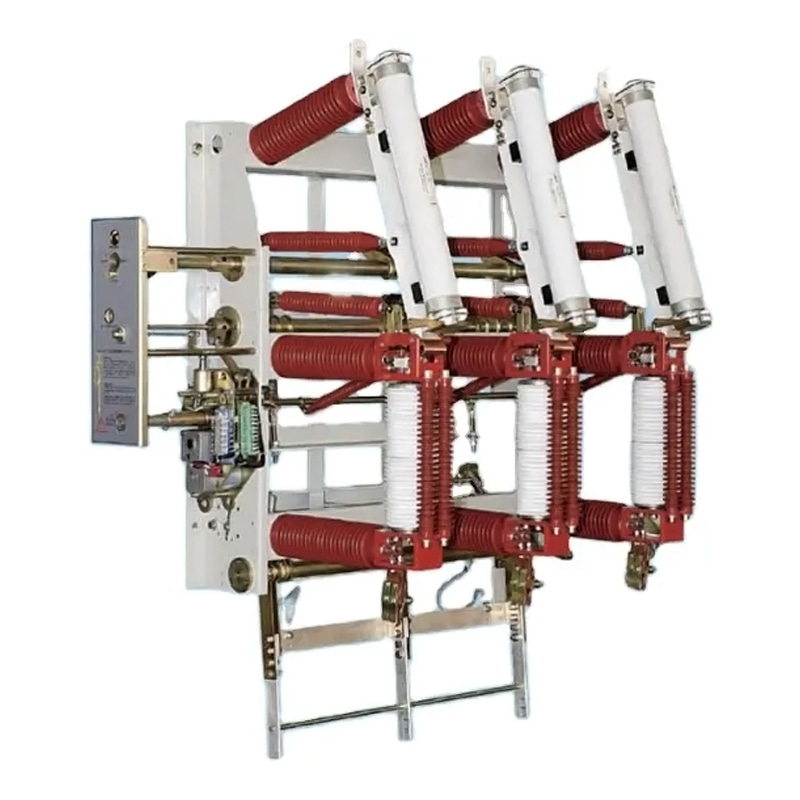
Regular maintenance of a load break switch is vital for system reliability, operational efficiency, and personnel safety. Inspection, cleaning, testing, and proper lubrication prevent premature wear, improve switching performance, and extend service life. Qinghang Electric Co., Ltd. offers high-quality outdoor load break switch and high voltage load break switch, along with detailed maintenance guidance to support safe and efficient operation.
1. Establish a Comprehensive Maintenance Schedule
Creating a structured maintenance schedule is the initial step:
Daily or Weekly Visual Checks: Inspect for signs of damage, corrosion, dirt accumulation, or unusual mechanical wear.
Monthly Mechanical Checks: Operate switches to verify smooth movement of operating rods, hinges, and levers. Any abnormal resistance or grinding noises should be investigated immediately.
Semi-Annual Electrical Tests: Conduct insulation resistance tests, continuity checks, and arc-quenching verification.
Annual Full Inspection: Include contact surface measurements, arc chamber evaluation, and environmental impact assessment.
A consistent schedule helps detect problems early, reducing downtime and repair costs.
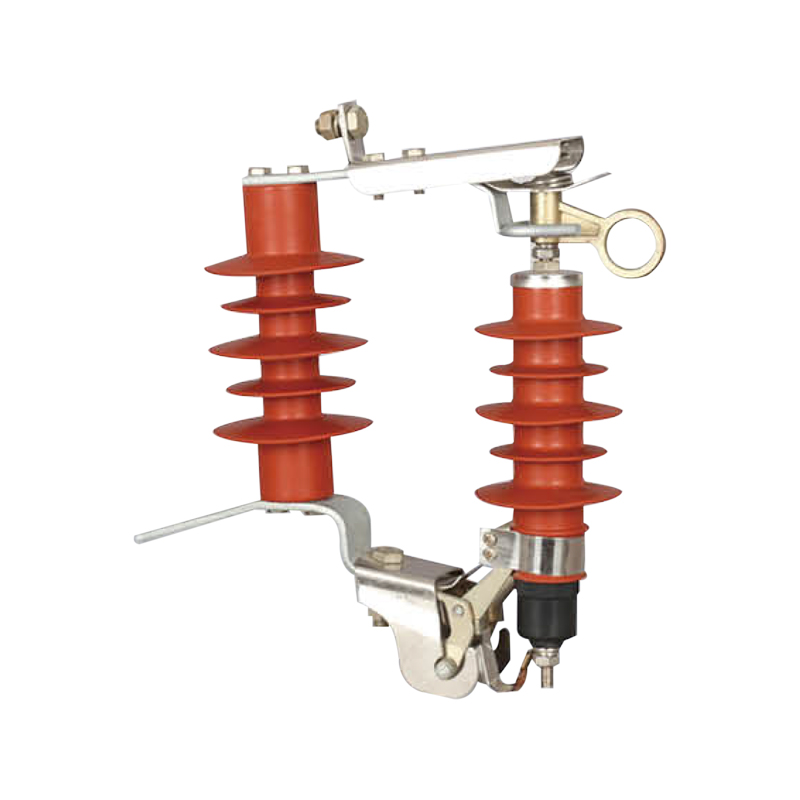

2. Detailed Mechanical Inspection
Mechanical reliability is critical for high voltage load break switches:
Operating Mechanism: Check for alignment of all moving parts. Misaligned components can prevent complete contact closure, result in arcing and contact erosion.
Contact Wear: Inspect contacts for pitting, oxidation, or uneven wear. Replace or resurface contacts showing significant damage.
Lubrication: Apply manufacturer-approved lubricants to mechanical joints and moving parts. Avoid over-lubrication, which can attract dust and reduce electrical contact quality.
Spring Tension and Alignment: Ensure operating springs are correctly tensioned for consistent switching force.
3. Electrical Inspection and Testing
Insulation Resistance: Use a megohmmeter to detect moisture, pollution, or insulation degradation. High resistance values indicate good insulation.
Arc Quenching Verification: For vacuum interrupters, confirm the vacuum integrity; for SF6 switches, check gas pressure and perform leak detection tests.
Connection Integrity: Ensure all cable and busbar connections are tight, clean, and free from corrosion. Loose connections may cause overheating and early failure.
Voltage and Current Checks: Verify that switches are operating within rated voltage and current limits.
4. Environmental and Site Considerations
Pollution and Dust: In areas with high pollution or dust, clean insulators and moving parts more frequently to prevent tracking and reduced insulation performance.
Moisture and Humidity: Use protective covers or shelters for outdoor switches in wet environments.
Temperature Extremes: Inspect for material expansion or contraction that could impact alignment or operation.
Pests and Debris: Prevent birds, leaves, or other debris from interfering with switch operation or contacts.
5. Operational Testing and Verification
No-Load Operation: Cycle the switch several times without load to ensure smooth operation and proper contact engagement.
Load Operation (If Safe): When permissible, conduct controlled load switching tests to verify arc-quenching performance.
Interlocks and Safety Devices: Confirm that grounding switches, safety locks, and mechanical interlocks are functioning correctly to prevent unsafe operation.
6. Common Maintenance Issues and Troubleshooting
Contact Erosion or Pitting: Often caused by frequent switching under heavy load; solution: inspect regularly and resurface contacts as needed.
Mechanical Binding: Usually from misalignment or dirt; solution: clean, lubricate, and adjust moving parts.
SF6 Gas Leakage: Detectable through pressure drop or leak detection equipment; solution: repair seals and recharge gas according to manufacturer guidelines.
Insulation Degradation: Often caused by moisture or contamination; solution: clean insulators, check seals, and replace degraded parts.



 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى