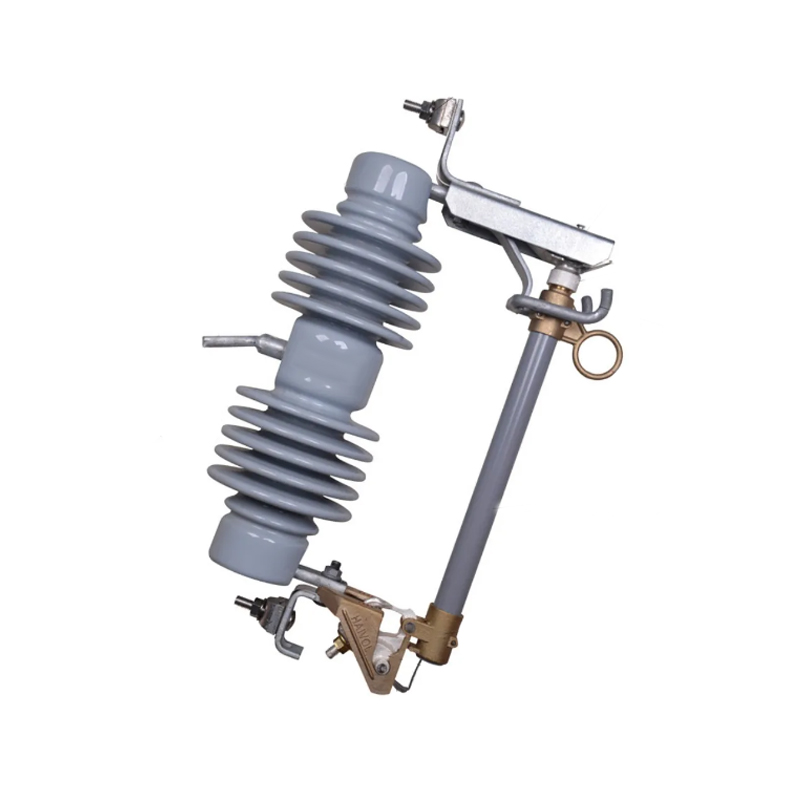
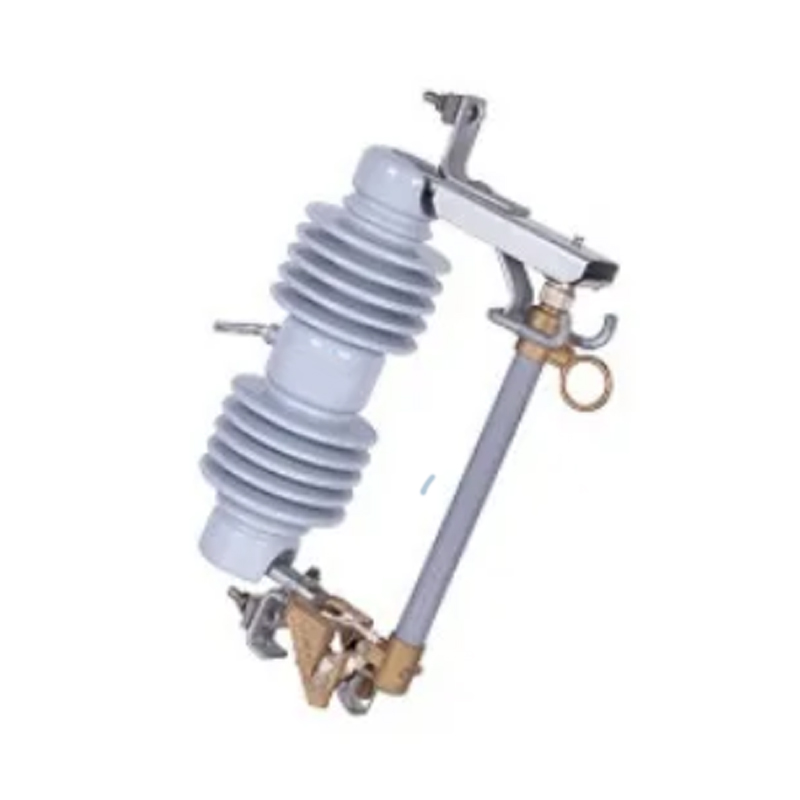
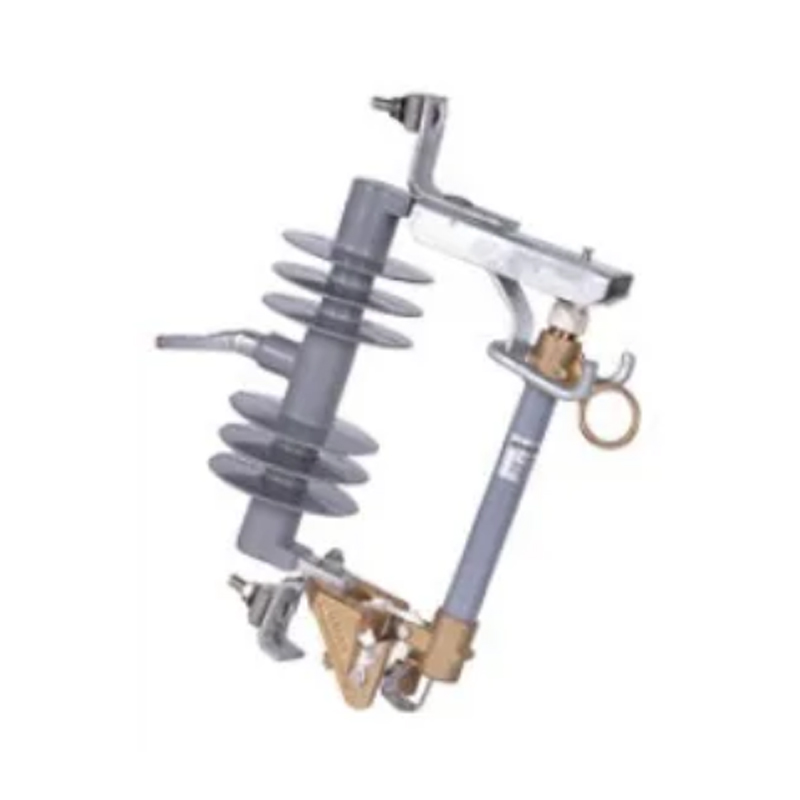
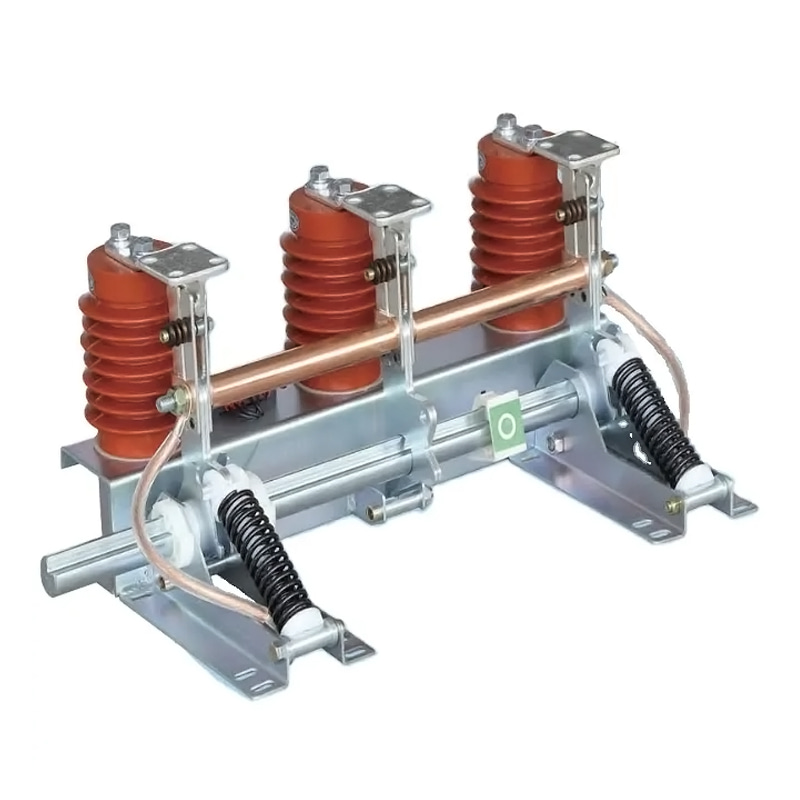
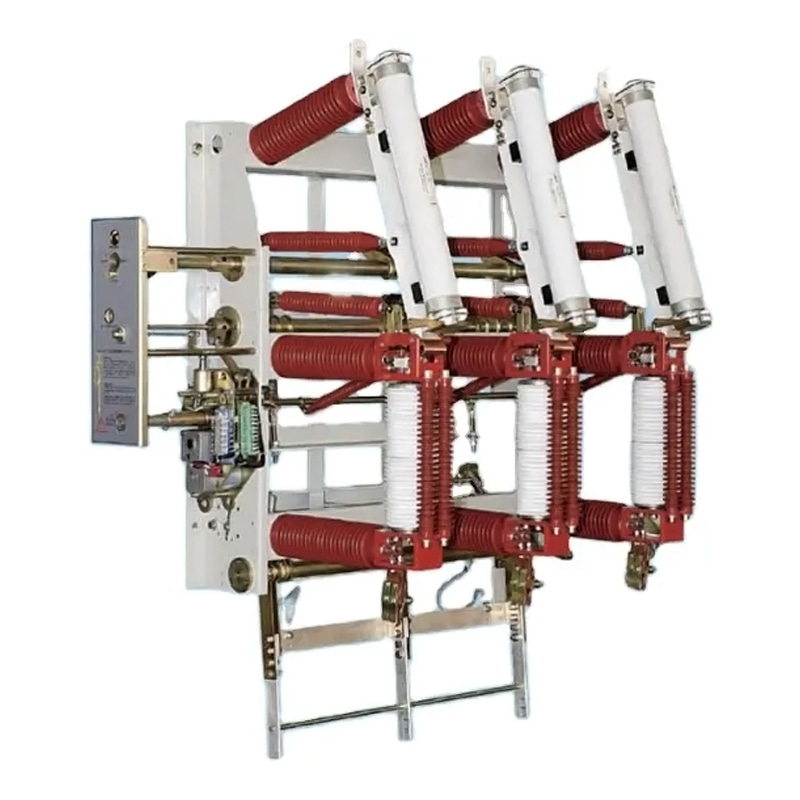
In the current landscape of electrical infrastructure, compliance with safety standards is essential. At our Load Break Switch Factory, we design load‐break switches to meet recognized global safety norms. Similarly, as an earthing switch manufacturer, our products are engineered in line with international and regional codes governing earthing and protective switches.
1. The Role of Global Safety Standards
1.1 IEC & ANSI/IEEE Standards
Designing switchgear for medium voltage and low voltage networks requires adherence to well‑established safety standards.
IEC 60364 provides comprehensive rules for low‑voltage installations, including protective grounding, overcurrent protection, and device selection.
For medium voltage switchgear, IEEE/ANSI C37.20.7 defines arc‑resistance ratings to ensure containment of fault energy without endangering operators.
These standards require that electrical disconnects and earthing devices meet essential performance, labeling, testing and design criteria.
1.2 Safety Practices & Workplace Codes
In North America, NFPA 70E and OSHA 1910.269 establish protocols for safe operation, maintenance, and handling of medium‑voltage equipment above 600 V. Approach boundaries, lock‑out/tag‑out procedures, and personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements are explicitly defined to reduce risk.
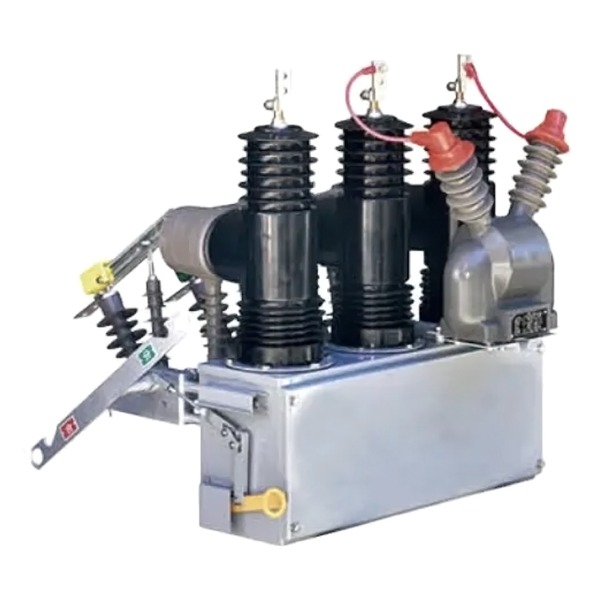

2. Key Design Considerations for Safety Switches
2.1 Load Break Switch Design
As a load break switch factory, our design process integrates:
Load interruption ratings to ensure safe switching under load without arc or contact welding
Mechanical interlocks compliant with IEC EN 62271‑200 to prevent hazardous misuses
Insulation and enclosure design to withstand fault currents and environmental stresses
We also conduct tests aligned with IEEE standards to verify arc flash performance and electrical endurance.
2.2 Earthing Switch Features
As an earthing switch manufacturer, safety is our priority. Our earthing switch designs include:
Fast and reliable grounding contacts rated for short‑circuit currents
Interlock mechanisms to ensure earthing cannot be engaged unless the circuit is de‑energized
Clear labeling and operating instructions meeting ANSI/NEMA symbol standards
These steps align with recognized safety precaution methods for earthing operation.
3. Quality Assurance and Certification
3.1 Management Systems and Audits
To assure compliance and consistency, we operate under ISO 9001 quality management standards, and our processes meet environmental and occupational health policies under ISO 14001 and ISO 18000. These systems ensure product traceability, batch control, and defect prevention.
3.2 Certification Evidence
We maintain CCC (China Compulsory Certification) and ISO documentation to show that each switch unit meets electrical safety performance tests. This gives both domestic and overseas clients confidence in our reliability.
4. Operational Training and Safe Use
4.1 Proper Installation and Maintenance
Factors like lock‑out/tag‑out, remote racking, and warning signage are critical. Safety switches must be installed within sight of controlled equipment per NEC Article 430.102(B) to enable secure maintenance.
4.2 Worker Training and PPE
Operators must understand safe approach boundaries—including distances up to several meters around energized parts—and follow arc flash and shock protection guidelines under NFPA 70E and OSHA regulations.
5. Benefits of Compliant Electrical Switch Design
Reduced risk to personnel: proper insulation, interlocks, and grounding lower accident chances
Regulatory acceptance: clients and authorities prefer compliant products
Operational durability: high‑quality switching components have longer life and less maintenance
Clear documentation: design, labeling, and test records aid audits and installation processes
Safety standards are not optional—they are foundational. If you value switches that meet design, testing, and performance expectations driven by safety regulations, we welcome you to connect with our engineering team.



 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى