Surge arresters and isolation switches are both integral components of modern electrical systems, offering essential protection and safety. Surge arrester factory and isolation switch manufacturer are crucial in providing high-quality, reliable products that ensure the longevity and safety of electrical networks.
Understanding Surge Arresters and Isolation Switches
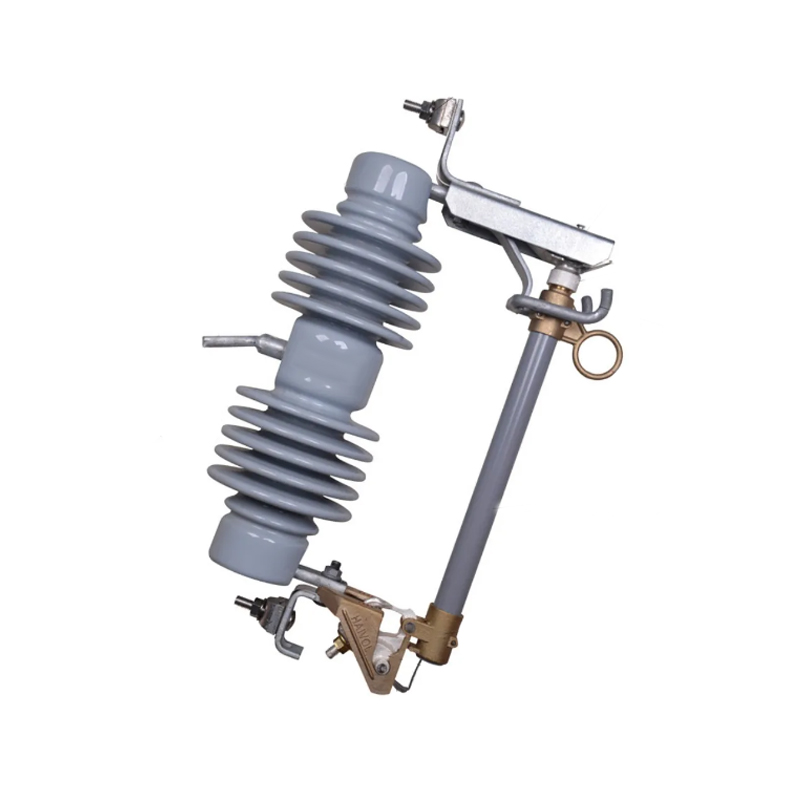
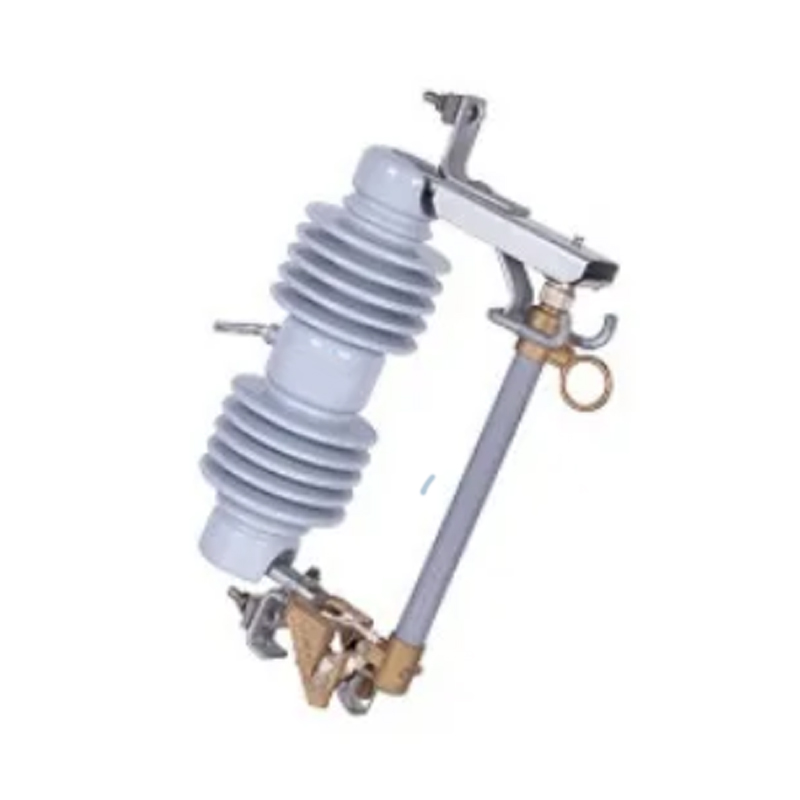
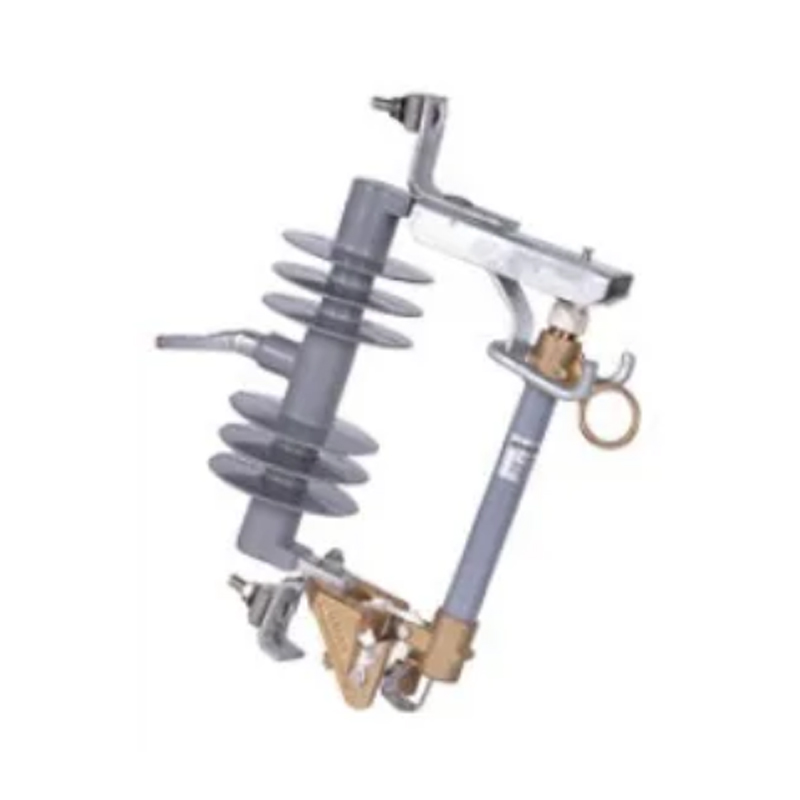
Surge Arresters are devices designed to protect electrical equipment from overvoltage caused by lightning or switching surges. These overvoltage events can result in severe damage to sensitive electrical components. Surge arresters are typically installed at strategic points in power distribution networks, including substations and electrical panels, to prevent such damage.
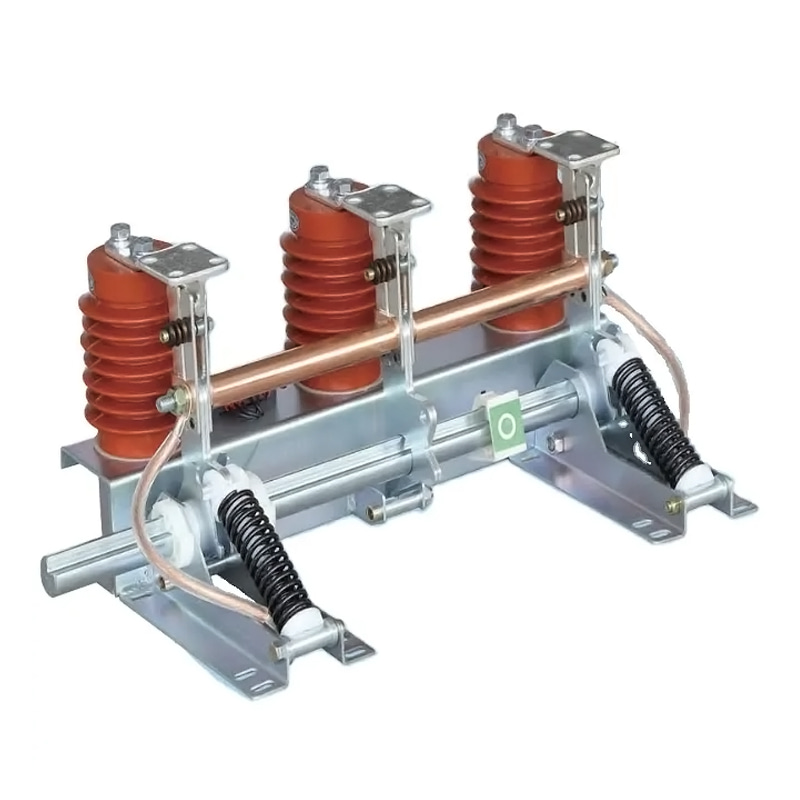
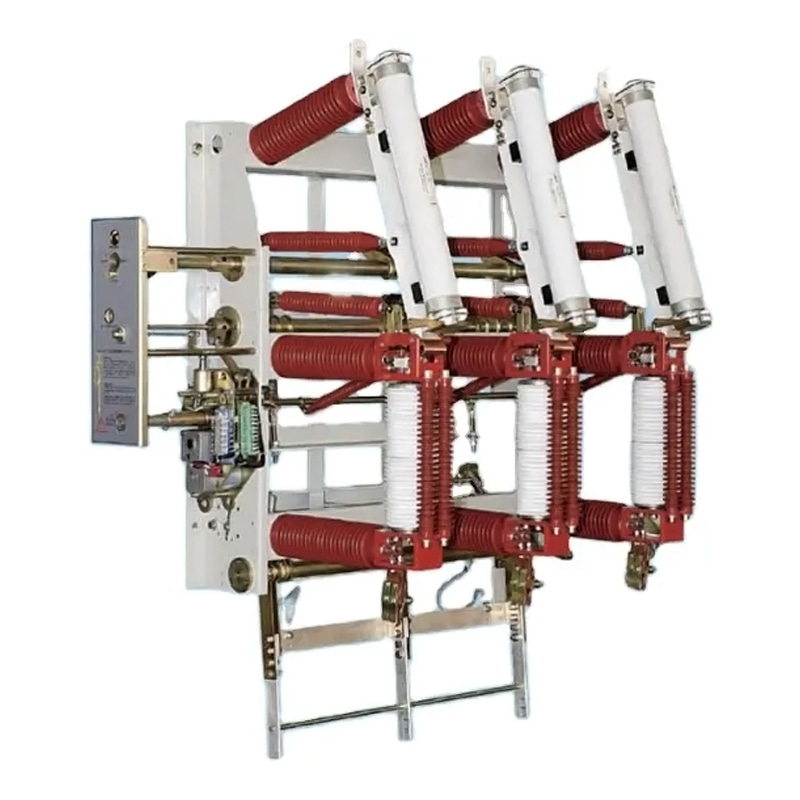
Isolation Switches, on the other hand, are used to isolate electrical circuits from the power supply for maintenance or in emergency situations. These switches are often found in distribution panels, substations, and electrical cabinets. Their primary role is to provide a visible break in the circuit, ensuring safety for personnel working on live equipment.
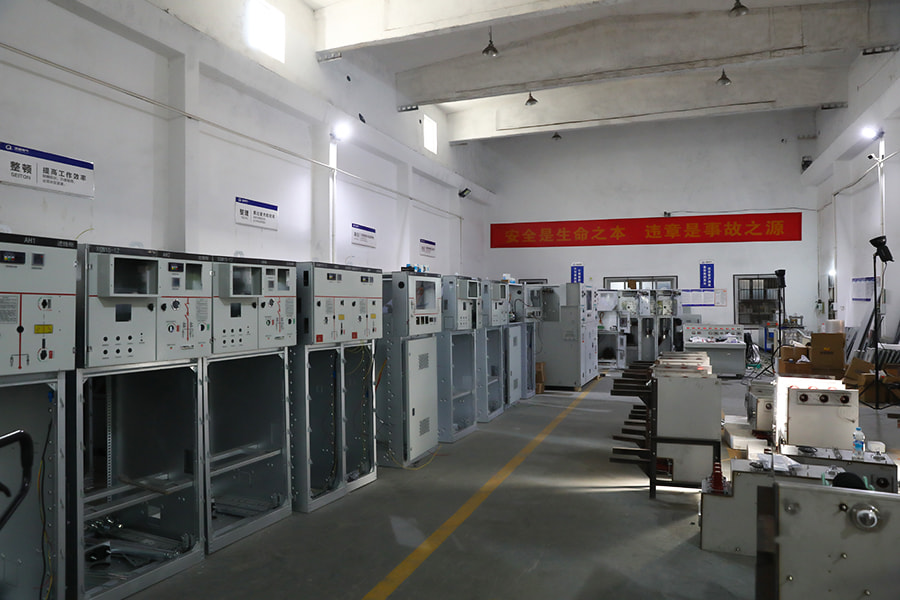

Applications of Surge Arresters and Isolation Switches
1. Surge Arresters in Power Distribution Networks
Power distribution networks are susceptible to lightning strikes and switching surges. These surges can cause irreparable damage to transformers, circuit breakers, and other sensitive equipment. Surge arrester factories play a vital role in producing surge arresters that are installed at key points in these networks to safeguard the entire system.
Substations: Surge arresters are often placed in substations where they protect transformers and other critical components from overvoltage surges caused by lightning strikes.
Residential and Commercial Buildings: Surge arresters are also installed in residential and commercial buildings, where they protect sensitive electronic devices such as computers, air conditioners, and security systems from transient voltage spikes.
2. Isolation Switches in Industrial Settings
In industrial electrical systems, the need for safety during maintenance is paramount. Isolation switch manufacturers produce devices that can completely disconnect a circuit from the power source, providing a secure environment for maintenance workers.
Maintenance and Repair: Isolation switches allow workers to isolate sections of the electrical system that require inspection or repair. This isolation ensures that no electrical current flows to the area under maintenance, protecting workers from potential electrocution.
Preventing Faults: These switches also help in preventing faults from spreading through the system by isolating the faulty sections quickly and efficiently. This is particularly important in high-voltage transmission systems, where a fault can result to widespread power outages or system failures.
3. Surge Protection in Renewable Energy Systems
With the increasing adoption of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power, surge protection has become even more critical. These systems often include sensitive equipment like inverters, controllers, and batteries, all of which can be damaged by electrical surges.
Solar Power Systems: Surge arresters are installed in solar power systems to protect inverters and controllers from lightning strikes and power surges that can occur during storms.
Wind Power Systems: Similarly, in wind farms, surge arresters are used to protect the turbines and control systems, which are often located in areas prone to lightning strikes.
Understanding the applications of these devices and their critical role in protecting electrical equipment from damage and ensuring worker safety highlights their importance in both residential and industrial settings. As technology evolves and electrical systems become more complex, the role of surge arresters and isolation switches will only continue to grow, offering enhanced protection against the increasing challenges posed by modern electrical environments.



 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى