Enhancing System Reliability with Earthing Switches
Earthing switches, also known as ground switches, are critical components in electrical systems, providing a means to safely ground or earth electrical equipment during maintenance or fault conditions.
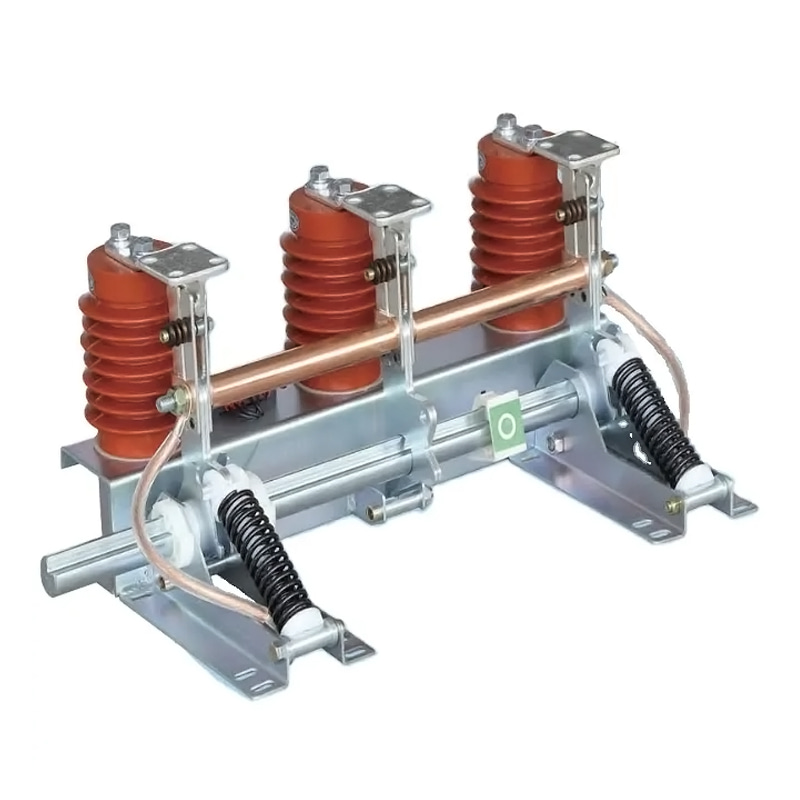
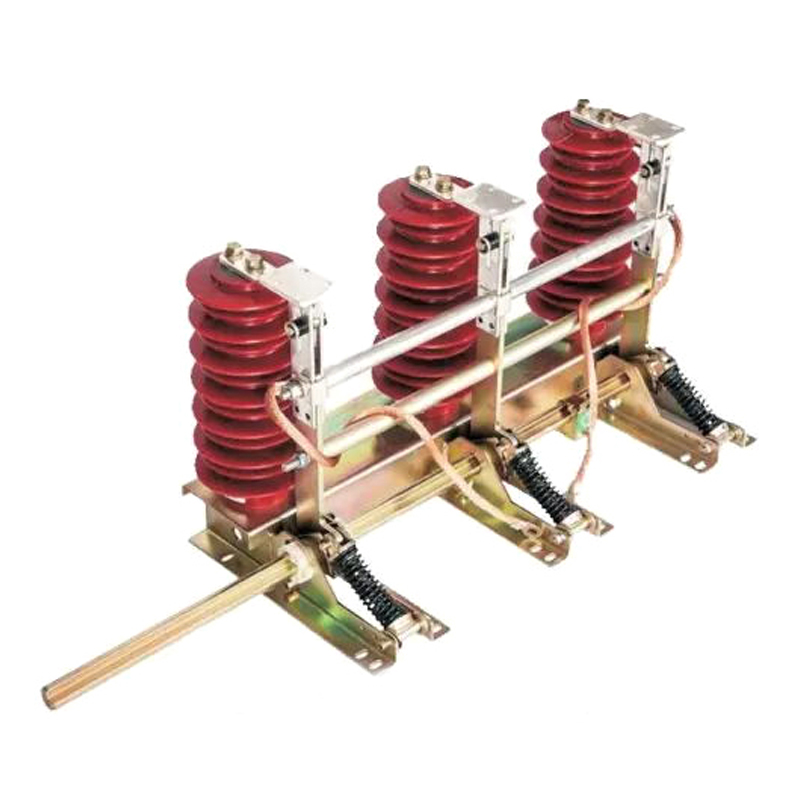
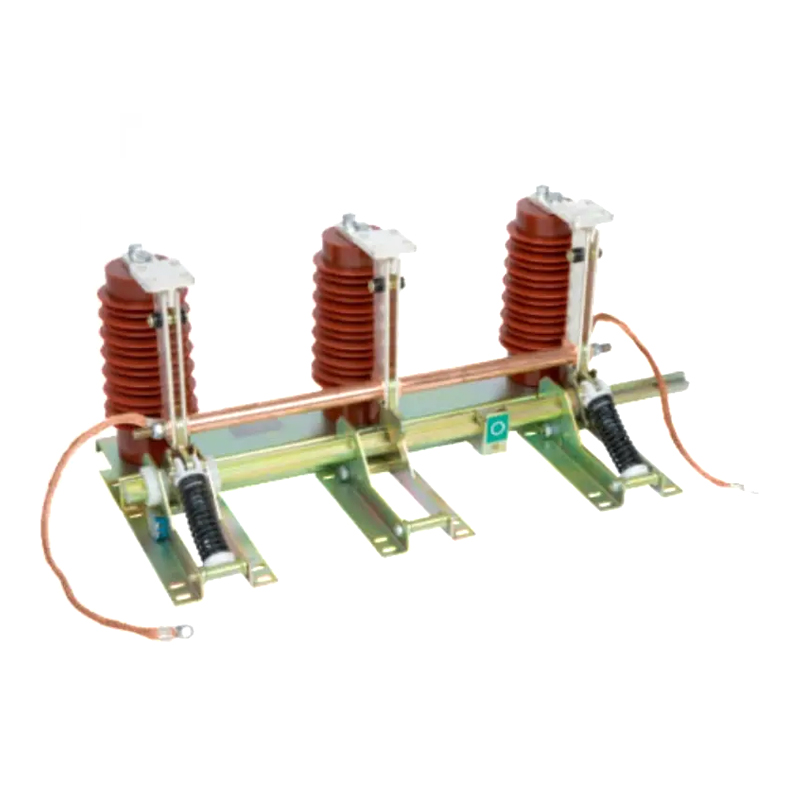
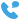
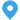
An earthing switch is primarily utilized for grounding or earthing electrical equipment during maintenance or fault conditions. It consists of a switch mechanism and grounding contacts enclosed within a protective housing. When activated, the switch establishes a low-resistance path to the ground, effectively grounding the equipment and ensuring the safety of personnel and the reliability of the electrical network. Earthing switches are commonly deployed in substations, switchyards, and other high-voltage installations.
Earthing switches are typically installed in substations, switchyards, and other high-voltage installations. They consist of a switch mechanism and grounding contacts housed within a protective enclosure. When activated, the switch closes, establishing a low-resistance path to ground for fault currents or induced voltages, effectively grounding the equipment.
One common application of earthing switches is in conjunction with Earth Trip Switches. Earth Trip Switches detect fault currents or leakage to earth and automatically trigger the earthing switch to isolate the faulty equipment, preventing further damage or hazards.
Regular inspection and maintenance of earthing switches are essential to ensure their proper functioning. This includes testing for proper operation, verifying the integrity of grounding contacts, and ensuring that the switch mechanism operates smoothly.
Earthing switches are indispensable components in electrical systems, providing essential grounding functionality to ensure the safety of personnel and equipment. Their deployment, along with regular maintenance and testing, contributes to the overall reliability and resilience of electrical networks.
The Functionality of Ground Switches in Electrical Grounding
Ground switches, also referred to as earth switches, are crucial components in electrical systems designed to establish a connection between electrical equipment and the earth or ground. Their primary function is to ensure the safety of personnel and equipment by providing a means to ground or earth electrical circuits during maintenance, repair, or fault conditions.
It comprises a switch mechanism and grounding contacts housed within a protective enclosure. When activated, the switch creates a low-resistance path to the ground, effectively grounding the equipment during maintenance, repair, or fault conditions. Ground switches are commonly installed in substations, switchyards, and high-voltage installations to ensure the safety of personnel and equipment. Regular maintenance is necessary to verify their proper operation and reliability.
Ground switches are typically installed in substations, switchyards, and other high-voltage installations where reliable grounding is essential. They consist of a switch mechanism and grounding contacts enclosed within a protective housing. When activated, the switch closes, creating a low-resistance path to ground for fault currents or induced voltages, effectively grounding the equipment.
One important aspect of ground switches is their coordination with Earth Trip Switches. Earth Trip Switches detect fault currents or leakage to earth and automatically trigger the ground switch to isolate the faulty equipment, preventing further damage or hazards.
Regular maintenance and testing of ground switches are crucial to ensure their proper functioning. This includes checking for proper operation, inspecting grounding contacts for damage or wear, and verifying the integrity of the switch mechanism.
Ground switches are essential components in electrical systems, providing vital grounding functionality to safeguard personnel and equipment. Their deployment, along with effective maintenance practices, contributes to the overall safety and reliability of electrical networks.



 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى