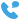
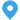
Key Components and Functions of a Transformer Substation
A transformer substation is a critical component of the electrical power distribution system. It is designed to transform voltage from high to low, or vice versa, to facilitate the efficient transmission and distribution of electricity. Typically, transformer substations are situated in strategic locations to serve urban, suburban, and industrial areas, ensuring a stable and reliable supply of electrical power.
The primary components of a transformer substation include power transformers, circuit breakers, disconnect switches, and protective relays. Power transformers are pivotal as they step down high-voltage electricity from transmission lines to lower voltages suitable for consumer use. Circuit breakers and disconnect switches play crucial roles in managing the electrical load and ensuring safety during maintenance or fault conditions. Protective relays, on the other hand, monitor the system for anomalies and trigger protective measures to prevent damage to the equipment and the network.
Transformer substations come in various configurations and sizes, depending on their location and the specific needs they serve. In urban settings, they are often housed in buildings or underground to small their footprint and reduce visual impact. Rural substations, however, may be more expansive and exposed due to available space and lower population density.
The integration of modern technology in transformer substations enhances their efficiency and reliability. Automation and remote monitoring systems allow operators to manage and troubleshoot the network more effectively, ensuring small downtime and prompt response to any issues. Moreover, advancements in transformer materials and design contribute to improved performance and reduced energy losses.
Transformer substations are indispensable for managing the voltage levels in power distribution networks, ensuring that electricity is delivered safely and efficiently to end users.
Enhancing Electrical Distribution with Compact Secondary Substations
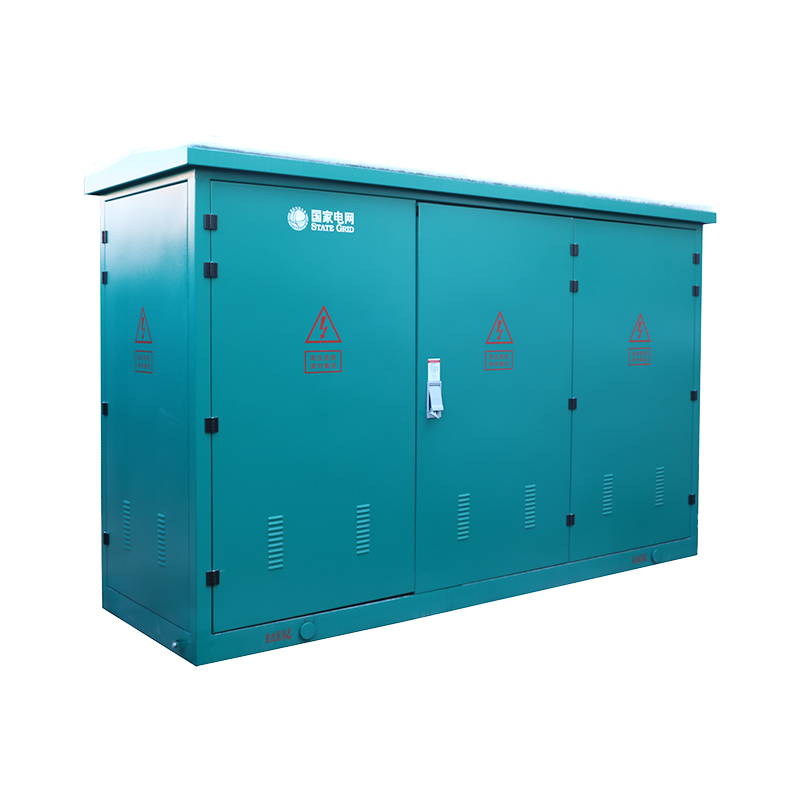
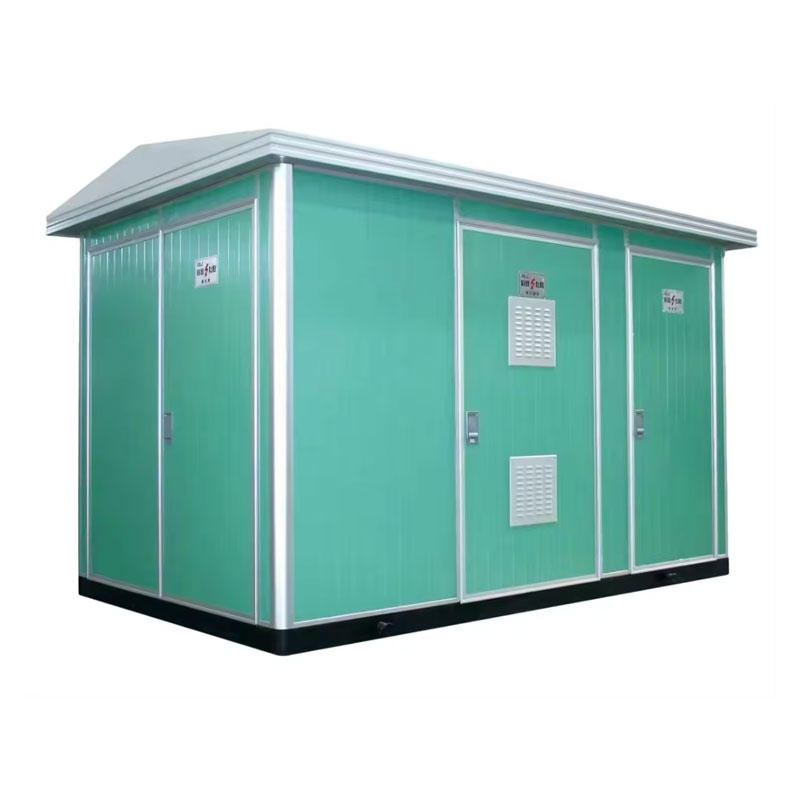
A compact secondary substation (CSS) is an innovative solution in the realm of electrical distribution, offering a streamlined and efficient approach to managing power supply. Designed to integrate seamlessly into urban and industrial environments, CSS units provide a crucial link between the high-voltage transmission network and low-voltage consumer distribution.
The primary advantage of CSS lies in its compact and modular design. Unlike traditional substations, which require substantial space and infrastructure, a CSS can be installed in confined spaces, such as within buildings, underground, or in areas with limited available land. This adaptability makes CSS units particularly valuable in densely populated urban areas where space is at a premium.
A typical CSS consists of a transformer, medium-voltage switchgear, low-voltage switchboard, and protection and control devices, all housed within a single enclosure. The enclosed design not only protects the equipment from environmental factors and vandalism but also enhances safety for personnel and the public. Furthermore, the prefabricated nature of CSS units allows for quick installation and commissioning, reducing downtime and operational disruptions.
Efficiency and reliability are key attributes of compact secondary substations. By placing the transformer and associated switchgear near, CSS units small power losses that occur during electrical transmission. Additionally, modern CSS designs incorporate advanced monitoring and control systems, enabling remote operation and real-time performance tracking. This capability ensures prompt identification and resolution of issues, thereby maintaining a consistent and reliable power supply.
Compact secondary substations represent a forward-thinking approach to electrical distribution. Their space-efficient, modular design, combined with advanced technological features, makes them an ideal choice for modern urban environments.



 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى